Learning from Each Other
Peer-to-peer (P2P) exchanges have become a cornerstone of innovation in state transportation agencies. Designed to share knowledge, test new approaches, and strengthen collaboration, these exchanges help DOTs tackle complex challenges while improving performance and outcomes. At the federal level, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) encouraged these activities through its Every Day Counts (EDC-7) and other programs, promoting the rapid adoption of proven innovations. Each state supports these efforts through its State Transportation Innovation Council (STIC), which serves as a hub for fostering cross-agency collaboration, knowledge transfer, and the adoption of new strategies.
At NJDOT, P2P exchanges do more than fulfill federal guidance—they provide a practical mechanism for advancing internal collaboration, building external partnerships, and piloting solutions that enhance safety and infrastructure resilience. Through structured exchanges with local, regional, and national partners, NJDOT has accelerated implementation of innovations ranging from rural roadway safety improvements to digital twin modeling for traffic management. These forums also create opportunities for centralized data sharing, coordinated planning, and the development of problem-solving methods that can be adapted across divisions and partner agencies.
NJDOT’s experience demonstrates how peer exchanges can translate shared knowledge into measurable outcomes, from cost savings and improved safety to more effective planning and operations. NJDOT first hosted a Peer Exchange in October 2001, aligning research management practices with department goals/policies. Additional goals include collaborating with TRB, NCHRP, and other universities (NJDOT 2001). NJDOT followed this with another Peer Exchange Report in 2006, centered on how NJDOT can better implement research findings and establish performance standards, highlighting lessons learned from states like Delaware, North Carolina, and Minnesota (NJDOT 2006). The Department went on to publish an October 2011 Peer Exchange Report, highlighting recent improvements, such as the use of the automated PROMPTS (Project Management and Progress Tracking System) system to help better track project progress from problem statement to delivery (NJDOT 2011).
In June 2014, FHWA hosted a Peer Exchange on Locally Administered Federal-Aid Projects, sharing NJDOT’s Local Aid Eligibility Assessment form as a model example. State officials also noted their desire to create a certification acceptance program with USDOT (FHWA 2014). The Department then hosted another Research Peer Exchange in October 2016, which promoted linking financial data to performance goals, and was held alongside the Annual Research Showcase to maximize stakeholder input (FHWA 2016).
Strengthen Collaboration Within NJDOT
Improving Rural Road Safety
Rural road departures—where vehicles unintentionally leave the roadway—pose a significant safety risk, often resulting in fatalities or serious injuries. In 2018 and 2019, NJDOT, in partnership with FHWA, hosted a peer exchange with Cumberland and Somerset counties to explore strategies for reducing these incidents (NJDOT BRIIT, 2020).
County engineers discussed approaches such as rumble strips, high-friction surface treatment (HFST) on curves, and improved roadway markings. By sharing their experiences and local data, participants identified which countermeasures were most effective under various conditions.
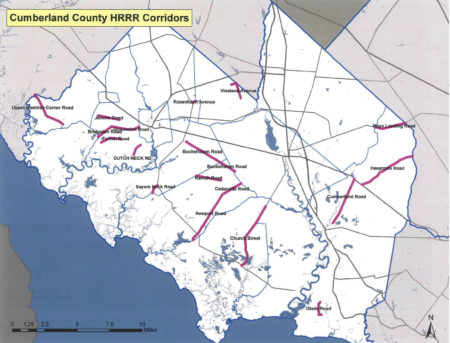
To move from discussion to implementation, NJDOT and the South Jersey Transportation Planning Organization (SJTPO) identified pilot locations on High Risk Rural Roads (HRRR). Several roads in Cumberland County were subsequently designated HRRR and received targeted safety improvements. The exchange also brought to light implementation challenges, including a shortage of specialized contractors, high unit costs for HFST, and outdated crash data. Somerset County engineers reported using FHWA’s HFST Curve Selection & Installation Guide to prioritize projects and manage costs effectively.
Peer exchanges helped NJDOT and its county partners turn shared safety expertise into targeted improvements on rural roads—directly reducing crash risk in New Jersey communities (NJDOT BRIIT 2020).
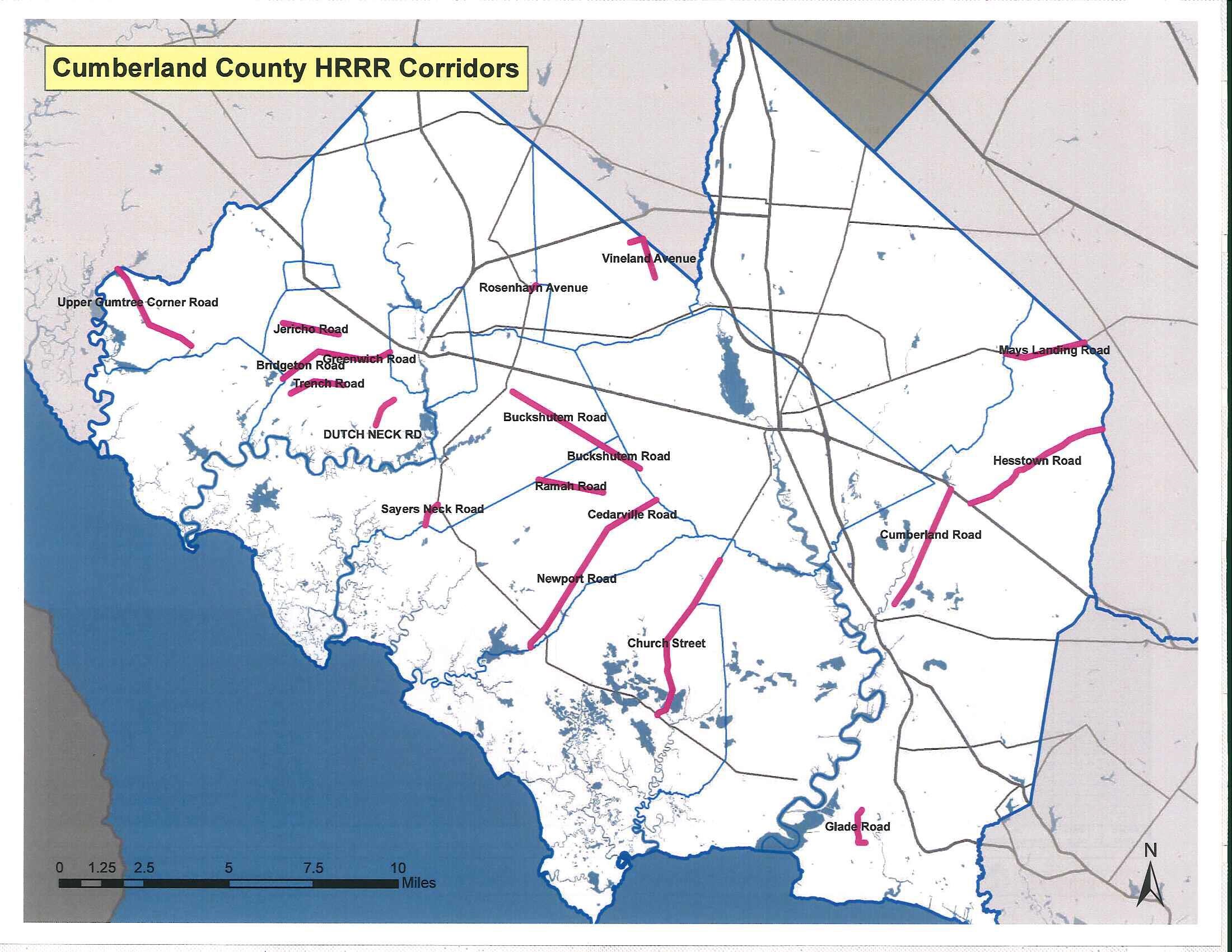
HFST improvements on five curves along a mile-long stretch of Chimney Rock Road (Somerset County) reduced annual crashes by 84 percent, falling from 73 to just 12. Other rural roads in the county experienced reductions of up to 80 percent.
Building on these results, the County is incorporating GIS-based crash mapping and the Regional Curve Inventory and Safety Assessment to identify and prioritize future high-risk locations for signage or HFST. Staff are also using FHWA guidance to help select and implement the most appropriate curve treatments.
The exchange allowed counties not only to learn new approaches but also to plan more efficiently and anticipate challenges before implementation. The collaborative process strengthened NJDOT’s internal coordination and set a model for county-level safety projects across the state.
Rebuilding Infrastructure Through Cross-Agency Collaboration
In July 2025, NJDOT partnered with the New Jersey Department of Community Affairs (NJDCA) and the New Jersey Infrastructure Bank (I-Bank) to help Seaside Park rebuild its storm-damaged boardwalk. While not a traditional peer exchange, this project illustrates the same principles of shared knowledge, aligned resources, and collaborative problem-solving (NJIB 2025).

Boardwalks are essential transportation assets in coastal communities, supporting pedestrian mobility, emergency response access, and local economies. The I-Bank provided $12.3 million in low-interest financing over 30 years, while NJDCA connected local needs with available funding. NJDOT estimates the project will save approximately $5.1 million for taxpayers and support 147 direct construction jobs. Some of the project’s major design upgrades include replacing the substructure of the boardwalk to improve resiliency, and adding new ADA-compliant ramps to ensure the boardwalk can be enjoyed by all users.
By treating boardwalks as essential transportation corridors, peer-style collaboration helped turn shared expertise into a project that saves money, supports jobs, and strengthens coastal access.
Beyond financial benefits, the project offers lessons in streamlining multi-agency coordination, expediting project delivery, and applying NJDOT expertise at multiple levels. NJDOT Commissioner Fran O’Connor stated that the project is “a perfect example of how multiple state agencies can work together to deliver smart, lasting infrastructure improvements in coordination with a local government” (NJDOT LARC 2025).
Working with External Partners
Sustaining TSMO
Transportation Systems Management and Operations (TSMO) strengthens safety and mobility by using technology, data, and operational strategies to improve performance on the existing roadway.
In early 2025, the National Operations Center of Excellence (NOCoE) hosted a Sustaining TSMO Virtual Peer Exchange to share best practices nationwide. NJDOT was invited to present how it continues to elevate TSMO within the organization. Senior Director of Transportation Mobility Sal Cowan described NJDOT’s evolution from establishing a 24/7 Transportation Management Center to embedding TSMO principles across every division (NOCoE 2025).
Cowan emphasized that sustaining TSMO strategies requires long-term relationships with partners such as FHWA, MPOs, university researchers, and neighboring DOTs. These collaborations allow the Department to integrate real-time and historical data into planning, leading to coordinated roadway operations and enhanced safety outcomes across modes.
TSMO is also incorporated into long-range planning, including freight strategies and electric vehicle initiatives. NJDOT is investing $40 million in work programs focused on staff training, emerging technologies, and operational readiness. These commitments position the Department to continuously adapt to new challenges—while ensuring TSMO remains embedded in everyday practice.
One TSMO project grew directly from lessons learned through peer exchanges. In 2019, the NCHRP Management and Use of Data for Transportation Performance Management guide highlighted how NJDOT’s progress in training staff, joining probe-data user groups, and learning from agency peers already using the Regional Integrated Transportation Information System (RITIS) and INRIX platforms (NCHRP 2019).
After joining the I-95 Corridor Coalition’s Probe Data Analytics User Group, NJDOT staff observed how Maryland and other DOTs used probe data to track congestion and manage projects. That experience helped staff adopt similar in-house methods. By 2022, these lessons led to national recognition, as NOCoE awarded NJDOT “Best TSMO Project” for its U.S. Route 1 ITS Improvement Project in South Brunswick. The project reduced PM-peak travel times by 45 percent and delays by nearly 30 percent (NJDOT BRIIT 2022).
Sustaining TSMO demands shared strategies, shared data, and shared commitment—peer exchanges help keep all three in motion.
Extending Pavement Life With Balanced Mix Design

In March 2023, FHWA convened eight Northeastern transportation agencies for a peer exchange on Balanced Mix Design (BMD), a method of asphalt performance testing that reduces cracking and extends service life. NJDOT shared its use of BMD for specialty mixtures, applying AASHTO-certified testing standards to benchmark performance while maintaining volumetric testing using state and third-party labs. Sampling occurs approximately every 3,500 tons, with plans to increase frequency (FHWA 2023).
The exchange highlighted regional approaches to data management, verification, and validation. NJDOT refined testing methods, reduced quality assurance costs, and evaluated a broader range of conditions for specialty asphalt mixes. NJDOT’s BMD initiatives have extended pavement life. High-performance thin overlays (HPTO) mixes have lasted up to 13 years on higher-distress pavements, and combining Binder Rich Intermediate Course (BRIC) with stone matrix asphalt (SMA) has increased projected service life by at least 10 years compared to traditional mixtures with no BRIC. The collaboration reinforced the value of sharing technical expertise across state lines (Hajj & Aschenbrener 2021).
Innovative asphalt testing means longer-lasting roads and smarter spending.
Planning for the 2026 World Cup
With New Jersey hosting seven matches and the final for the 2026 World Cup, NJDOT engaged in extensive planning and coordination. In October 2024, the agency coordinated with NOCoE to host a peer exchange with other state DOTs and host cities to discuss large-scale event strategies. Lessons drawn from Georgia DOT’s Super Bowl LIII and Miami-Dade County’s Copa 2024 guided approaches to security, transit scheduling, and traffic management, including hard-shoulder running lanes. Locally, NJDOT is coordinating security upgrades with the New Jersey State Police, syncing transit schedules with the Port Authority, and collaborating with multiple local agencies (NOCoE 2025).
Ahead of the World Cup, NJDOT is advancing several Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) upgrades to support real-time traffic management. ITS includes tools such as dynamic message signage and computerized arterial traffic signals (NJDOT 2025). NJDOT has awarded $20.6 million in contracts for ITS improvements in Bergen, Hudson, Essex, and Passaic counties (NJ Office of the Governor 2025). As part of this suite of upgrades, NJDOT is developing a first-of-its-kind LiDAR 3D roadway map of the area surrounding MetLife Stadium to enhance operations and incident response. The exchange demonstrated how P2P collaboration can accelerate innovation, anticipate challenges, and enable technology-driven solutions in high-pressure, large-scale scenarios (HNTB 2025).
Planning for international events pushes innovation, collaboration, and real-time problem-solving.
Applied Research and Performance Tracking
In September 2017, Montana DOT hosted a peer exchange focused on applied research, performance measure tracking, and implementation of innovative practices. NJDOT participated virtually, sharing its approach to integrating implementation into research projects (Seeber & Hirt 2018).
Participants discussed funding strategies, aligning project with FHWA criteria, and systems for tracking outcomes, such as Minnesota’s ARTS database. NJDOT drew lessons on improving internal tracking, pairing performance outcomes with reporting, and maintaining financial sustainability while adopting new practices. These insights have informed NJDOT’s approach to research integration and long-term planning.
Lessons Learned and Opportunities Ahead
NJDOT’s experience shows that structured peer collaboration advances innovation, improves safety, and leads to measurable results. Through internal and external exchanges, NJDOT has:
- Strengthened safety on rural roads through targeted countermeasures
- Reduced costs and supported job creation through municipal infrastructure projects
- Enhanced operational strategies through TSMO integration and digital mapping
- Extended pavement life using advanced asphalt design and testing
- Improved planning and coordination for large-scale events like the 2026 World Cup
- Refined research implementation and performance tracking for long-term planning
These efforts have helped NJDOT shift from traditional traffic and asset management toward a proactive, knowledge-driven approach. Lessons learned inform decision-making in storm resiliency, freight planning, electric vehicle strategies, and municipal collaboration.
Looking ahead, NJDOT will continue to integrate peer exchanges into long-range planning, freight operations, and EV initiatives. National resources, including the NCHRP synthesis on peer exchanges, offer further guidance for maximizing collaboration and innovation.
Peer exchanges turn shared knowledge into tangible results—safer roads, smarter projects, and more efficient operations.
In March of 2025, NJDOT’s Bureau of Research, Innovation, and Information Transfer (BRIIT) participated in a peer exchange focused on research strategies, project selection, and implementation (MassDOT 2025).
NJDOT is also contributing to best practices for emerging technology. In early 2025, NJDOT took part in the Artificial Intelligence in State DOTs peer exchange sponsored by Caltrans (Caltrans 2025). Discussions centered on workforce readiness, data governance, ethical guidance, and real-word applications of AI in transportation. New Jersey already has a statewide AI policy, and NJDOT is applying these concepts through a staff-facing chatbot and a pilot integrating machine learning into construction cost estimation.
An October 2025 AI-focused peer exchange convened by University of Massachusetts – Amherst reinforced the importance of collaboration as states adapt to rapidly evolving technologies. NJDOT played a central role, contributing to the national dialogue and helping shape best practices. With no federal regulatory framework yet in place, states are using peer exchanges to align strategies, address challenges, and learn from each other. More broadly, peer exchanges allow NJDOT to share its experience and translate collective knowledge into practical improvements across operations, research, and technology adoption.
Resources
Caltrans Division of Research, Innovation & System Information. (2025). AI in State DOTs Peer Exchange 2025 Final [PDF]. Retrieved from https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/lgdkkepqv8q70nm8nswmz/AI-in-State-DOTs-Peer-Exchange-2025-FINAL.pdf?rlkey=5uuavev1qkjxskr85hznsp0lq&e=1&st=ozc4pnex&dl=0
Federal Highway Administration. (2023). Northeast Peer Exchange on Balanced Mix Design (BMD): Outcomes and summary. https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/pavement/asphalt/HIF_2023%20Northeast_Peer_Exchange_on_Balanced_Mix_Design_%28BMD%29_Outcomes_and_Summary.pdf
Hajj, E. Y., & Aschenbrener, T. B. (2021, March). Case studies on the implementation of balanced mix design and performance tests for asphalt mixtures: New Jersey Department of Transportation (NJDOT) (WRSC-TR-21-06). University of Nevada, Reno. Retrieved from https://eng.auburn.edu/research/centers/ncat/files/New-Jersey-Case-Study.pdf
HNTB Corporation. (2025) Garden State Glory: As a host to FIFA World Cup 26™ games and final, New Jersey is meticulously preparing its transportation infrastructure for global visitors while ensuring smooth mobility for locals. https://www.hntb.com/think/garden-state-glory/
Massachusetts Department of Transportation. (2025). MassDOT Research Peer Exchange 2025: Final Report. Retrieved from https://www.mass.gov/doc/massdot-peer-exchange-report/download
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. (2019). Management and Use of Data for Transportation Performance Management: Guide for Practitioners (NCHRP Report 920). Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/25462
National Operations Center of Excellence. (2024, October 14–15). WC26 New Jersey peer exchange: October 14–15, 2024. https://transportationops.org/pse/wc26newjersey
National Operations Center of Excellence. (2025, March 11). Sustaining TSMO Peer Exchange Report. https://www.transportationops.org/system/files/uploaded_files/2025-03/NOCoE%20-%20Sustaining%20TSMO%20Peer%20Exchange%20Report.pdf
New Jersey Department of Transportation, Bureau of Research, Innovation & Information Transfer. (2020, March 26). How New Jersey counties are reducing rural roadway departures. NJDOT Technology Transfer. https://www.njdottechtransfer.net/2020/03/26/how-new-jersey-counties-are-reducing-rural-roadway-departures/
New Jersey Department of Transportation, Bureau of Research, Innovation & Information Transfer. (2022, June 9). NJDOT wins Best TSMO Project from National Operations Center for Excellence. NJDOT Technology Transfer. NJDOT Technology Transfer. https://www.njdottechtransfer.net/2022/06/09/njdot-wins-best-tsmo-project/
New Jersey Department of Transportation, Local Aid Resource Center (LARC). (2025, July 17). Multi-agency collaborative effort delivers first boardwalk loan to Seaside Park. https://njdotlocalaidrc.com/news/post.php?s=2025-07-17-multi-agency-collaborative-effort-delivers-first-boardwalk-loan-to-seaside-park
New Jersey Department of Transportation. (2025). Traffic engineering (ITS/ MSE) – Division of Engineering: Electrical/ITS. https://www.transportationops.org/publications/new-jersey-dot-mobility-and-systems-engineering
New Jersey Infrastructure Bank. (2025, July 17). Multi-agency collaborative effort delivers first boardwalk loan to Seaside Park. https://www.njib.gov/news/multi-agency-collaborative-effort-delivers-first-boardwalk-loan-to-seaside-park-68793024d3c4b
New Jersey Office of the Governor. (2025, July 10). ICYMI: NJDOT’s FY25 capital program delivers more than $1 billion in contracts for the 7th consecutive year demonstrating Murphy Administration’s commitment to infrastructure investment. https://www.nj.gov/governor/news/news/562025/approved/20250710b.shtml
Seeber, K., & Hirt, B. (2018, January). Montana Department of Transportation research peer exchange: Implementation, performance measures, and the value of research (Final Report No. FHWA/MT-18-001/9510-566). CTC & Associates LLC. https://www.mdt.mt.gov/other/webdata/external/research/docs/peer/2017_report.pdf
Whitaker, D. W. (2019). Systemic Safety Improvements: Cumberland County Engineering Department. https://www.njdottechtransfer.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Cumberland-Systemic.pdf