The Semi-Circular Bend (SCB) testing configuration was evaluated to determine its applicability to NJDOT Specialty Asphalt Mixtures. The SCB Flexibility Index utilizes a three-point loading arrangement to measure the fatigue cracking resistance of a semi-circular compacted asphalt specimen. A pre-cut notch in the specimen dictates where the crack initiates. The area under the load-displacement curve, known as fracture energy (Gf), and the post-peak slope of the load-displacement curve are used to calculate the SCB Flexibility Index (FI) value. In general, as the SCB FI value increases, the fatigue resistance of the asphalt mixture also increases.NJDOT Research
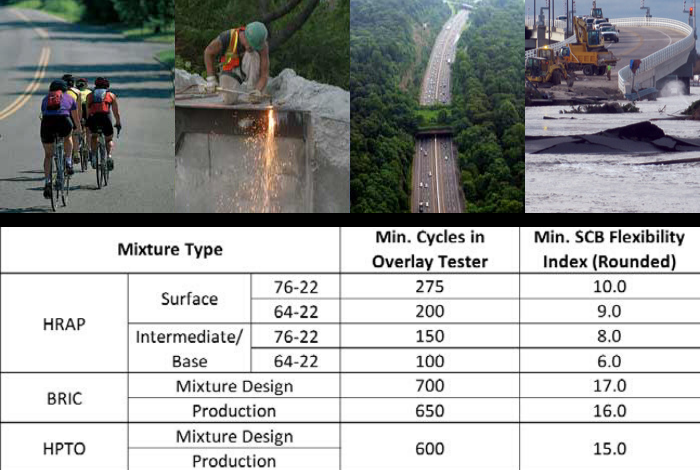
The study showed that the SCB FI test is highly influenced by the test temperature, loading rate, notch width and compacted air voids. The sensitivity to air voids was found to be counter-intuitive, such as when the air voids increase, the SCB FI value also increases. It is hypothesized that this is simply due to the additional air voids/air pockets increasing the “flexibility” of the asphalt mixture, thereby reducing the mixture stiffness. A large database was generated consisting of companion specimens tested in the Overlay Tester and the SCB FI tests. The database resulted in a strong correlation between the Overlay Tester and SCB FI, which in turn was used to develop tentative performance criteria for future adoption by the NJDOT. A round robin study was conducted to evaluate the expected repeatability of the SCB FI value. Five different laboratories were provided compacted gyratory specimens comprising of three different asphalt mixtures. The single operator coefficient of variation (COV%) was determined to be 21.5%, with the multiple operator COV% being 26.1%.
Posted in Uncategorized.
